Why Injection Molding is Essential for Mass Production
Introduction In the realm of mass production, efficiency and cost-effectiveness are paramount. Industries worldwide strive for manufacturing...
2 min read
Nick Erickson : Feb 20, 2025 11:43:11 AM
Material selection is a critical aspect of injection molding, influencing both the performance and cost of your final product. Whether you’re designing for commodity applications or high-performance needs in industries like automotive, medical, or aerospace, understanding the spectrum of material options is key to achieving the right balance of properties, durability, and manufacturability.
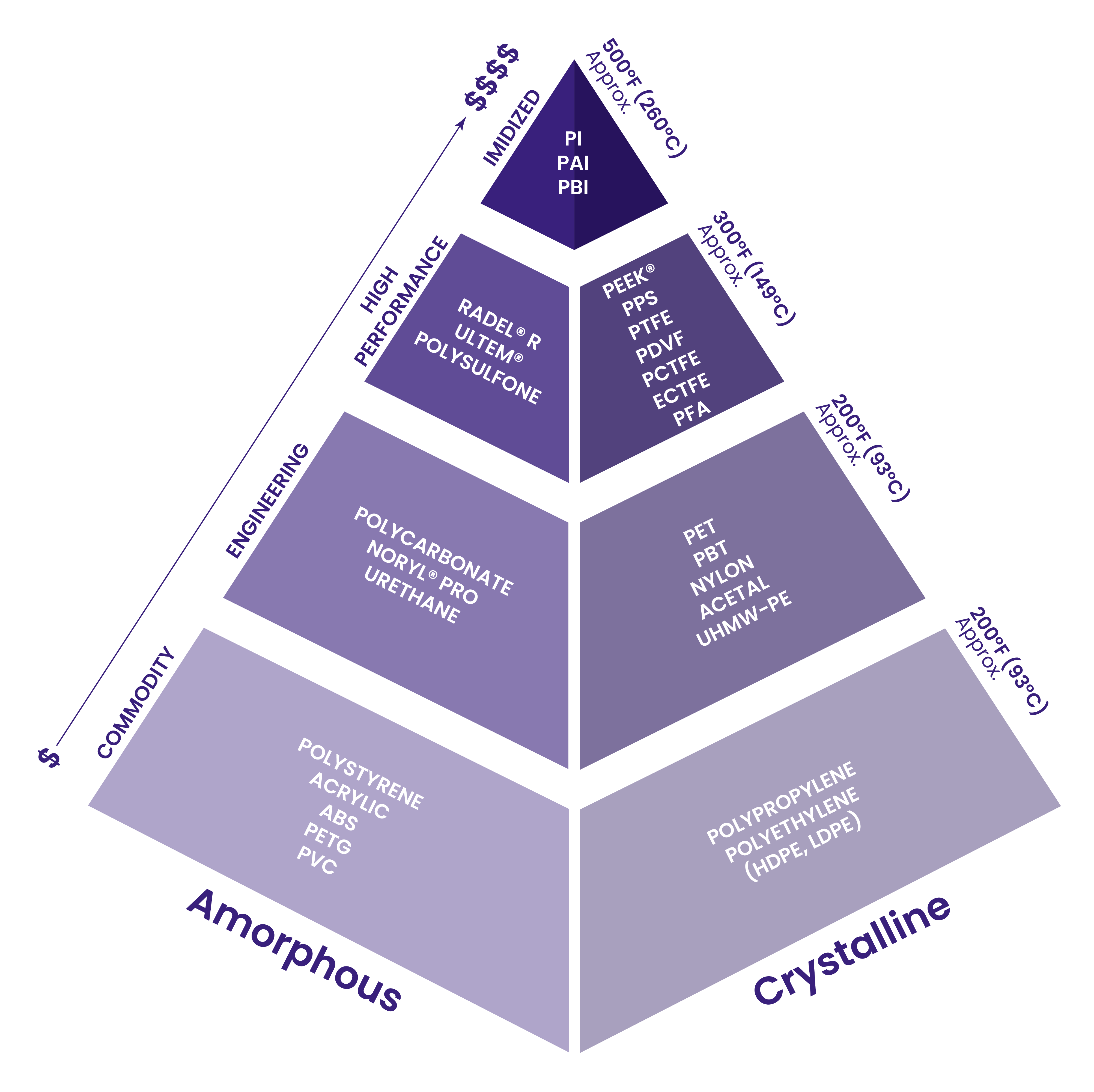
The material selection pyramid (featured above) provides a clear framework for categorizing injection molding materials by performance, cost, and thermal resistance. Here's how to navigate this landscape.
When selecting a material for injection molding, always begin by evaluating the specific demands of your application:
These requirements guide you toward the appropriate segment of the material pyramid.
The pyramid organizes materials into four main tiers, each with distinct properties and cost considerations:
Commodity Materials (Base Layer):
Ideal for general-purpose applications, commodity materials like polystyrene, acrylic, and ABS are cost-effective and suitable for low-stress environments. These materials work well in products like packaging, toys, or consumer goods.
Engineering Materials (Middle Layer):
Polycarbonate, nylon, and acetals fall into this category, offering improved strength, thermal resistance, and durability. These are perfect for applications like automotive components or industrial parts where higher mechanical performance is required.
High-Performance Materials (Upper Layer):
Materials like PEEK, polysulfone, and PPS excel in demanding environments. These materials are commonly used in aerospace and medical applications due to their exceptional heat resistance, chemical stability, and mechanical strength.
Mid-sized Performance (Peak of the Pyramid):
For the most extreme applications, materials like PI and PAI are used. While expensive, they can withstand temperatures of 500°F (260°C) or higher and provide unmatched performance in harsh conditions.
Cost is a significant factor in material selection. The pyramid visually demonstrates that as you move up, the performance of materials increases, but so does the price. Choosing the right material involves striking a balance between the cost of production and the functional requirements of the product.
For example:

Material selection doesn’t stop at choosing a resin from the pyramid. Prototyping and rigorous testing under real-world conditions are critical to confirm that your chosen material meets the functional and environmental demands of your product.
The material pyramid is a powerful tool for understanding and navigating injection molding material options. By aligning your application requirements with the properties and costs of materials, you can achieve optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
At Aprios, we specialize in helping designers and engineers select the right materials for their injection molding projects. Whether you need support with prototyping, design for manufacturing, or production planning, our team is here to help.
Contact us today to discuss your project and take the first step toward creating high-quality injection-molded products.
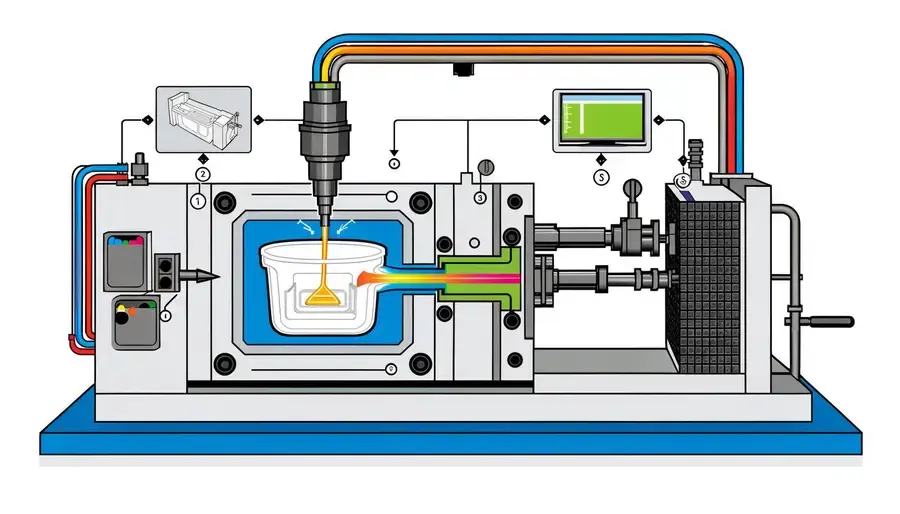
Introduction In the realm of mass production, efficiency and cost-effectiveness are paramount. Industries worldwide strive for manufacturing...
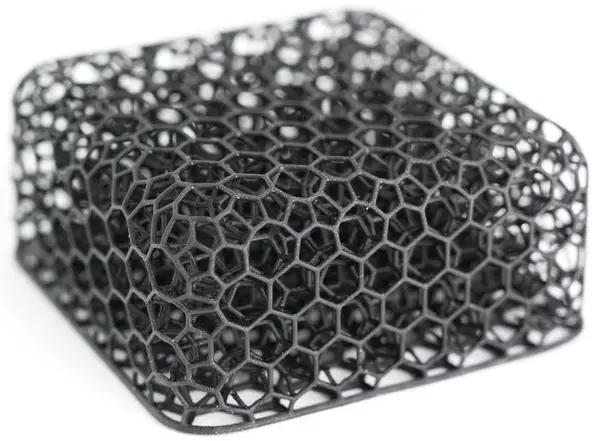
Additive manufacturing, especially through advanced methods like Carbon DLS, often comes with a higher price tag than more common 3D printing methods...

Why Does Additive Manufacturing with Carbon DLS Come with a High Price Tag? If you've ever dabbled in 3D printing or looked into it for your...